Binary Search
A tutorial on how to use binary search
Binary Search is a well known and essential algorithm in the field of competitive programming. Many coding problems feature binary search, so today, we shall learn it!
What is Binary Search?
Binary Search is a method used to quickly find an answer by splitting the interval (which you will search) into half. This is commonly used to find if specific values in a sorted array.
How is Binary Search Used?
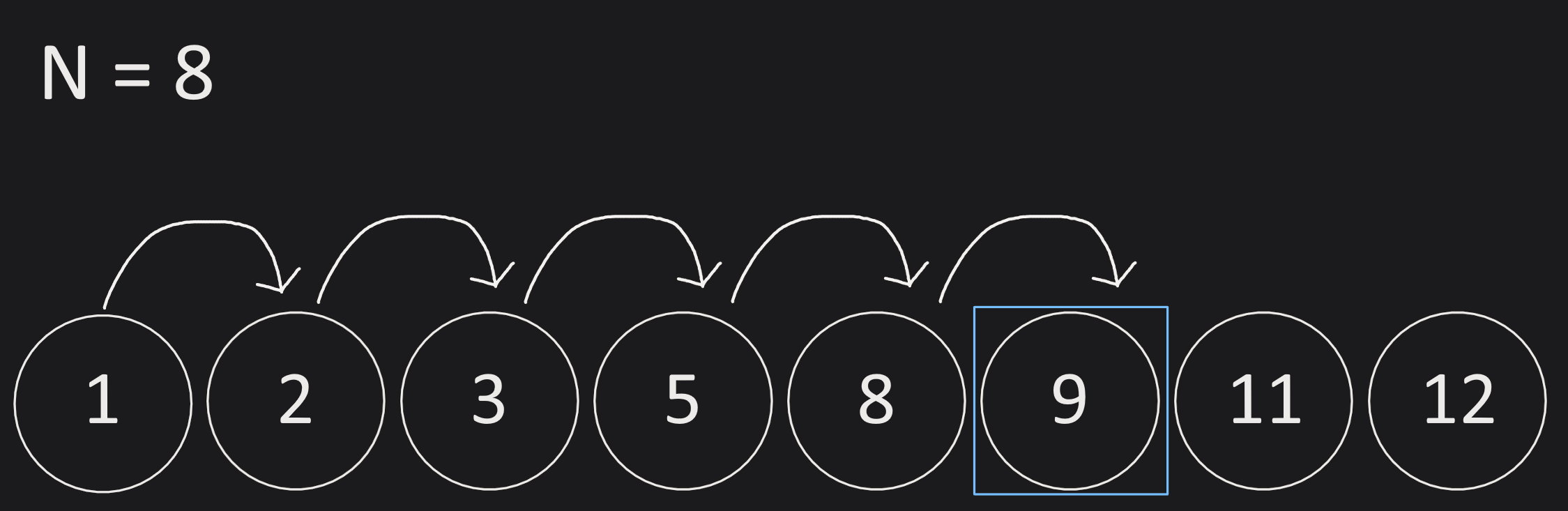
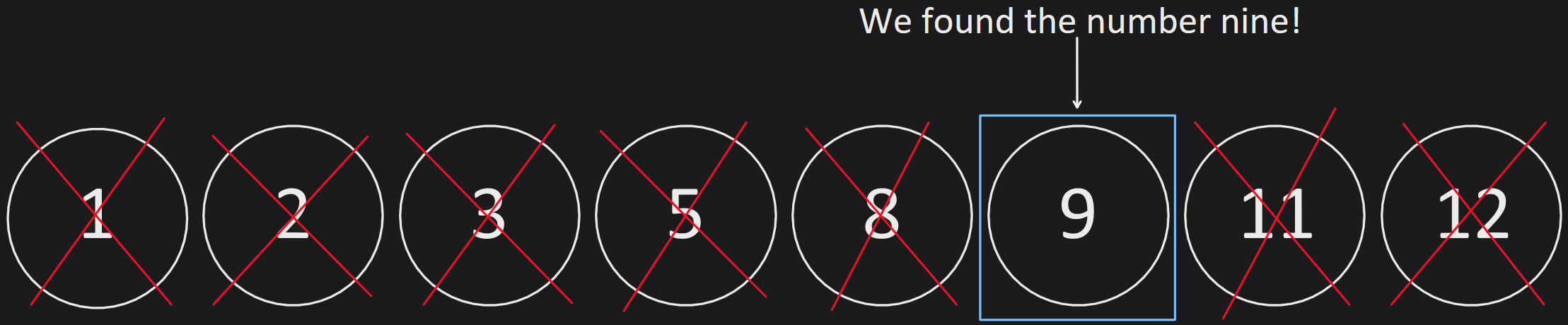
Let’s say you have a sorted array with some numbers:
You want to find the position where the number nine exists. We, as humans, can see that it is at position six from the left. However, how would we figure out where the nine is from a simple computer program?
Brute Force Solution
The simple solution is to check from the left and keep moving to the right until we find the number nine (or possibly a number larger than nine if nine does not exist in the array). This would take N operations (worst possible case) when N is the length of this array.
Binary Search Solution
We can go even faster using Binary Search. Because we know that this is a SORTED array, we can cut the range (we are looking in) in half if we still haven’t found our number.
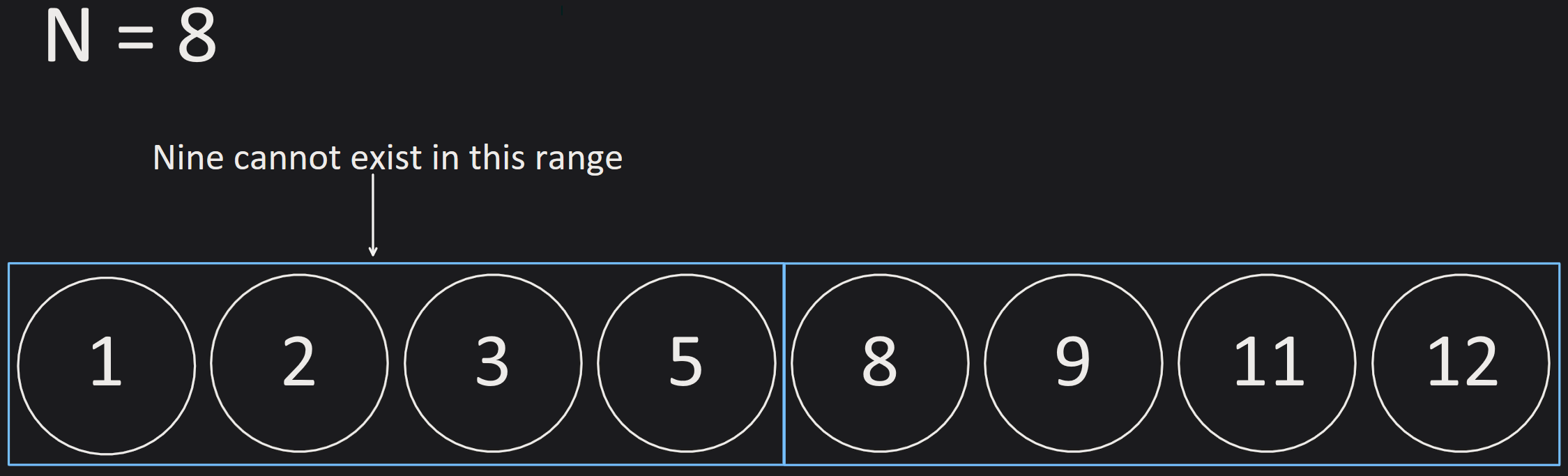
Let’s take the example from above. Our original range is [1, 8], because we are looking at the entire array for the number nine (the range consists of the positions of the numbers, not the numbers themselves).
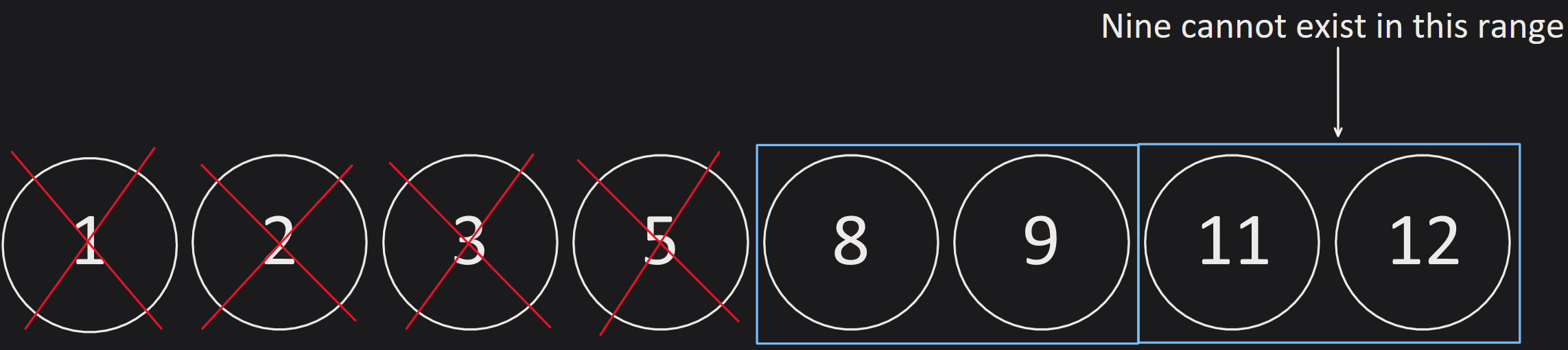
If we split this range in half, we get ranges [1, 4] and [5, 8]. The largest number in the left range is five (number on the fourth position), and the smallest number on the right is eight (number on the fifth position). We can see that nine can never exist on the left range because the maximum number of the left range in five, which is smaller than nine. We can therefore say that nine can only exist on the right range, changing our range to [5, 8].
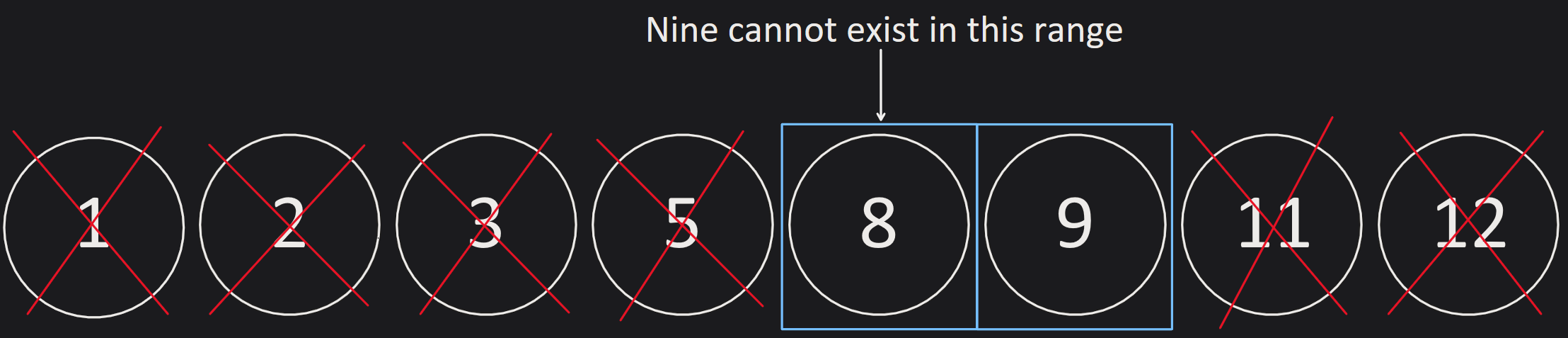
We can just continue this process until we find our number nine (or the range consists of only one number). This is how it would work if we continue:
Why does this work?
This solution works because the array is sorted. When the array is sorted, we can figure out if a number (in this case, nine) can or cannot exist on the left rnge when cutting our range in half.
Therefore, we can always cut our range in half until we have only one number left in our range: the number we wanted to find. The maximum number of operations is log2(N) because we always cut our range in half until the length of our range is one. Keep in mind that you might hear time complexities of log(N) from other sources. In competitive programming, people usually refer log2(N) as just log(N).
Conclusion
Binary Search can be used in many ways. The key theme of binary search is that at some point inside our range, something changes. In our instance above, numbers in positions one to five are less than nine, while the rest of the numbers on the right are larger then or equal to nine. We must have exactly one point that changes something when going from left to right (usually, we try to find that point while binary searching).
Make sure to mess around with Binary Search and see how you can use them in various scenarios.
Practice problems:
Here are some practice problems for Binary Search (many of these problems will use a form of binary search but will be harder than the example we used today):